Index of Economic Freedom
- Index of Economic Freedom is published by Heritage Foundation, an American think-tank.
- The Index covers 12 freedoms – from property rights to financial freedom – in 186 countries.
- The Index of Economic Freedom documents the positive relationship between economic freedom and a variety of positive social and economic goals.
- Economic freedom is measured based on 12 quantitative and qualitative factors, grouped into four broad categories of economic freedom:
- Rule of Law (property rights, government integrity, judicial effectiveness)
- Government Size (government spending, tax burden, fiscal health)
- Regulatory Efficiency (business freedom, labor freedom, monetary freedom)
- Open Markets (trade freedom, investment freedom, financial freedom)
- India moved up to the 130th spot, up from 143 in 2017.
- India's overall score increased by 1.9 points, led by improvements in judicial effectiveness, business freedom, government integrity, and fiscal health.
- Economic freedom is the fundamental right of every human to control his or her own labor and property.
Mahatma Phule
- Prime Minister paid tributes to Mahatma Phule on his birth anniversary recently.
- Phule was India’s first Dalit reformer who offered a systematic theory of caste.
- In the 19th century, Jyotiba Phule was the most radical opponent of untouchability and the caste system as he called for the complete demolition of its oppressive structure.
- The Maharashtrian reformer and his wife Savitrirao Phule opened the first-ever school for Dalit girls in 1848 in Pune.
- Gulamgiri (slavery) is one of the 16 books written by him which was dedicated to the African-American movement to end slavery.
- Phule led the foundation of Satyashodhak Samaj (‘Seekers of Truth’) in 1848 in a bid to attain equal social and economic benefits for the lower castes in Maharashtra.
Rare sculpture of Rudrama Devi’s ‘last battle’ discovered
- A sculptural slab carved in granite that has a life-size portrait of Kakatiya warrior queen Rudrama Devi was discovered by the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI).
- It was discovered in the sanctum sanctorum of Trikuta temple at Bekkallu village in Siddipet district of Telegana.
- The discovery has unraveled the mystery of her death who was killed during a war by her own subordinate chief kayastha king Ambadeva somewhere near Warangal.
- The portrait sculpture is a first of its kind that displays a fierce fighting scene between Rudrama Devi and Ambadeva.
- The Kakatiya dynasty was a South Indian dynasty whose capital was Orugallu, now known as Warangal in the State of Telegana.
- Rudrama devi was one of the very few women to rule as monarchs in India and promoted a male image in order to do so.
Guidance to increase support for breastfeeding
- World Health Organization (WHO) and the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) issued a new 10-step guidance to increase support for breastfeeding in health facilities recently.
- Health facilities provide the immediate health system platform to help mothers initiate breastfeeding within the first hour and breastfeed exclusively for six months.
- Breastfeeding all babies for the first 2 years would save the lives of more than 8, 20,000 children under age 5 annually, noted a release issued by the WHO.
- Key features of the Guidelines include
- Hospitals should have a written breastfeeding policy in place, required staff competencies.
- Hospitals should also have an antenatal and post-birth care, including breastfeeding support for mothers.
- It recommends limited use of breast milk substitutes, rooming-in, responsive feeding.
- Finally it stresses upon support when mothers and babies are discharged from hospital and also educating parents on the use of bottles and pacifiers.
- MAA – Mothers’ Absolute Affection, a nation-wide program for promoting breastfeeding is in place under the Ministry of Health and family welfare, in India.
Green Trains for Green India
- As per estimation, approx. 4,000 MT of human waste is discharged from train coaches every day.
- Indian Railways has provided about 1, 25,000 bio-toilets in its coaches till March 2018.
- With the proliferation of bio-toilets in 60% coaches commensurate human discharge in open, has been eliminated.
- “Bio-Toilet project” of Indian Railways is an innovative & indigenous development of technology.
- This technology is first of its kind being used by any railroad in the world for On-board accelerated digestion of human waste.
- The human waste discharged in the bio-toilets is acted upon by a colony of anaerobic bacteria that convert human waste mainly into water and small amount of bio-gases.
- The gases escape into atmosphere and waste water is discharged after chlorination onto the track.
- It was developed jointly by Indian Railways’ Engineers & DRDO’s scientists.
- It is one example where the technology developed for defence applications has been utilized for civilian purpose.
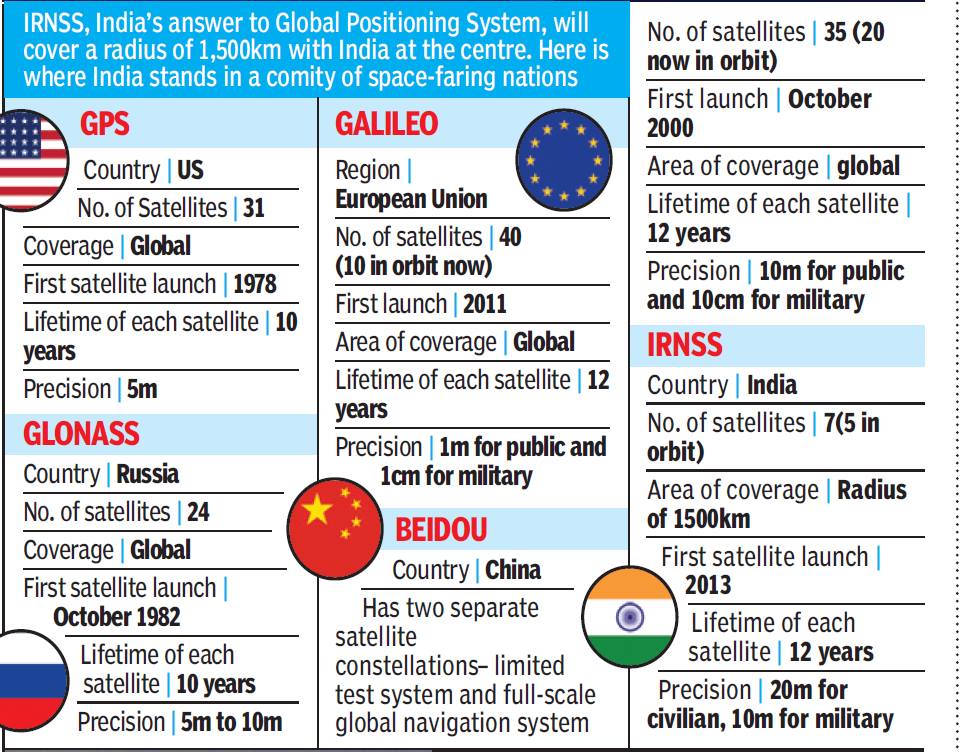
Indian Regional Navigation Satellite System 1I
- Navigation satellite IRNSS-1I was put in orbit by the Indian Space Research Organization’s (ISRO) PSLV-C41 rocket.
- The navigation satellites are meant for giving precise information of position, navigation and time of objects or people.
- The satellites will form the fleets of NavIC (Navigation with Indian Constellation).
- NavIC is being dubbed as India’s Own GPS.
- The satellites were built by a consortium of six Indian companies led by Alpha Design Technologies Ltd., Bengaluru.
- They have a civilian and a restricted military/security application.
- Like all other IRNSS satellites, IRNSS-1I will also carry two payloads
- Navigation payload former to transmit signals for determining position, velocity and time.
- Ranging payload for determining the frequency range of the satellite.
- Each satellite has a life span of 10 years.
- The system was planned to consist of 7 satellites (A,B,C,D,E,F,G) with 2 substitutes (H and I).
- Out of 7 satellites A, B, F, G will be in geosynchronous and C, D, E will be in geostationary orbit.
- IRNSS 1H, was unsuccessful as the satellite did not come out of its heat shield.
- While IRNSS 1I will replace IRNSS 1A as its three imported rubidium atomic clocks failed while in orbit.
Map of the Day
India Tiger Reserves
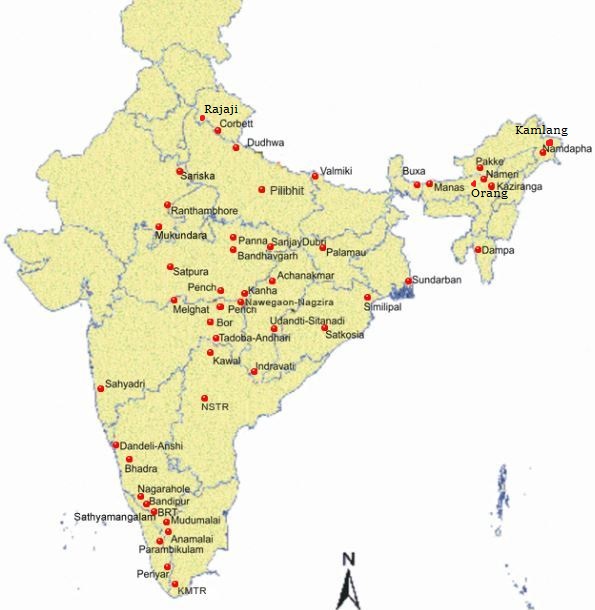
- In total, there are 50 tiger reserves in the country.
- Kamlang Tiger Reserve in Arunachal Pradesh is the 50th tiger reserve and latest addition in the country.
- The following are the states with only one tiger reserve
- Valmiki -Bihar
- Palamau- Jharkhand
- Dampa –Mizoram
- Nagarjunasagar Srisailam (NSTR)- Andhra Pradesh
- Amrabad Tiger Reserve was earlier part of Nagarjunasagar – Srisailam Tiger Reserve (NSTR) but, post-bifurcation, the northern part of the reserve is vested with Telangana and renamed as Amrabad Tiger Reserve and the southern part (NSTR) is with Andhra Pradesh.
- Jammu and Kashmir, Punjab, Himachal Pradesh, Haryana, Gujarat, Goa, Sikkim, Nagaland, Meghalaya, Tripura and Manipur are the states with no tiger reserves in their region.
- The tiger reserve in the four corner of our states
- Rajaji Tiger Reserve (Uttrakhand) -North
- Kalakad-Mundanthurai (KMTR) - South
- Namdapha (Arunachal Pradesh) - East
- Sahyadri (Maharashtra) – West
Source: PIB, The Hindu, Business standard
