Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW)
- OPCW is an independent, autonomous international organisation with a working relationship with the United Nations.
- It is the implementing body of the Chemical Weapons Convention (CWC), which entered into force in 1997.
- OPCW has 193 Member States working together to achieve a world free of chemical weapons.
- It is headquartered in The Hague, Netherlands.
- It was awarded Nobel Peace Prize in 2013.
- It has been recently granted additional powers by its members voting in two-third majority.
- Until now, OPCW could only say whether chemical weapons were used but not who had used them.
- The new power allows it to assign blame for attacks.
- This process of extending its jurisdiction was heavily opposed by Russia.
- But, Britain was supporting the move arguing that new powers were needed to deal with repeated chemical attacks in Syria.
RIMPAC
- RIMPAC (Rim of the Pacific Exercise) is the world’s largest international maritime exercise.
- The 26th edition of RIMPAC was hosted by the U.S. Indo-Pacific Command (INDOPACOM) recently.
- It commenced off the Hawaii coast with the participation from 25 countries.
- It is aimed at increased inter-operability and development of common understanding of procedures for maritime security operations.
- It provides a platform for multilateral operational interactions.
- India has participated in this edition and represented by INS Sahyadri.
- Israel, Sri Lanka and Vietnam joined RIMPAC for the first time.
- China is absent this year as it was dis-invited from participating by the U.S., citing China’s military actions in the South China Sea.
- China participated in the exercise in 2014 and 2016.
INS Sahyadri
- INS Sahyadri is an indigenously built stealth frigate.
- It participated in trilateral Malabar war games with Japan and the U.S. off the Coast of Guam.
- It recently participated in RIMPAC and has been adjudged runner-up in an innovation competition.
- INS Sahyadri presented the ‘idea of integrating yoga into our daily life as technology for well-being during extended deployments for ships’.
- The idea was appreciated by representatives of participating countries.
Mission Shaurya
- ‘Mission Shaurya’ is an initiative of the Tribal department of the Maharashtra State Government.
- It aims to train tribal students to scale Mt. Everest.
- Recently, 10 tribal students from residential schools in Chandrapur district of Maharashtra conquered Everest.
- Mission Shakti - Maharashtra government has also announced this mission to impart special training and prepare tribal students for the Olympics 2024.
International Organisation for Migration (IOM)
- IOM was established in 1951. It had been an observer to the UN since 1992.
- The agency joined the UN system as a related organization in September 2016.
- It is headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland.
- It works in the field of migration with governmental, intergovernmental and non-governmental partners.
- The organisation has 166 member countries (including India) and 8 observer states.
- It aims to provide humanitarian assistance to migrants in need, including refugees and internally displaced people.
- IOM works to help ensure the humane management of migration by providing services and advice to governments and migrants, promote international cooperation on migration issues.
- Mr. Vitorino of Portugal is the first Director General elected to IOM after it has become part of UN.
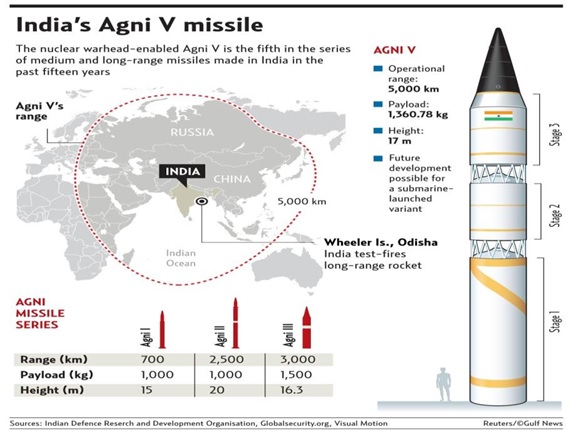
AGNI – V
- The Agni series (I to V) missiles constitute the backbone of India’s nuclear weapons delivery and part of nuclear triad.
- Agni-V is India’s longest-range ballistic missile which will be inducted into the nuclear arsenal soon.
- Earlier variants of the Agni family of long-range missiles have already been deployed.
- Agni – V is an Inter-Continental Ballistic Missile (ICBM) with a range of over 5,000 km and can reach most parts of China.
- It is powered by three stage solid fuelled missiles.
- It can carry a payload of 1.5 tonnes.
- It is a part of Integrated Guided Missile Development Program (IGMDP).
No-first-use doctrine
- India is committed to a ‘No-First-Use’ policy as part of its nuclear doctrine.
- Thus, second strike capability - the capability to strike back after being hit by nuclear weapons first becomes important.
Source: The Hindu, Indian Express
