Why in news?
In a recently released white paper, China announced that it would develop a Polar Silk Road (PSR).
What is the development in the Arctic region?
- Climate Change - The unintended consequences of climate change are contributing to the transition of the arctic region.
- Rising temperatures are melting some of the thick sheets of ice of the Arctic Ocean.
- This is exposing and making usable, some of the hitherto blocked up potential.
- Navigation - That, in turn, is opening channels through which ice-breaking ships can pass.
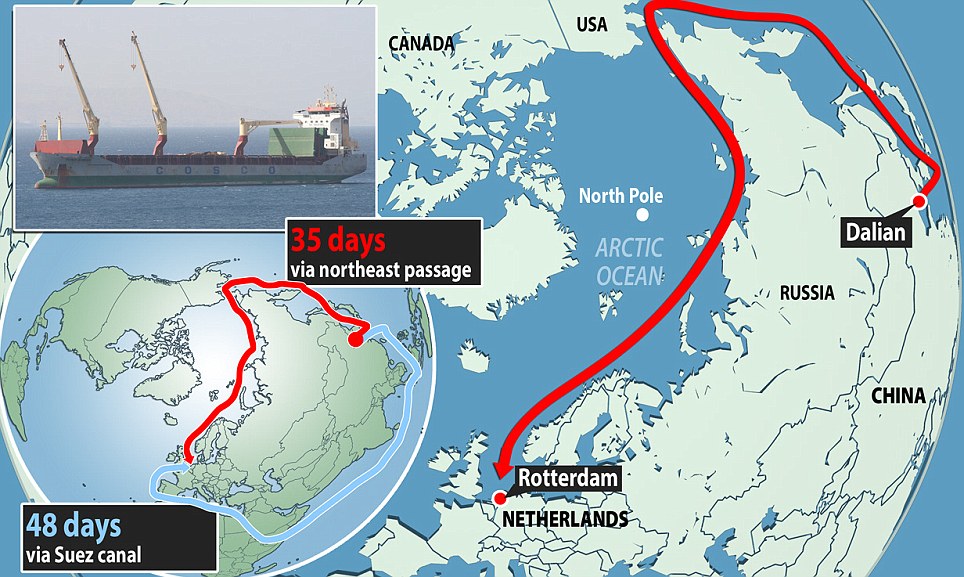
- Once it becomes navigable, commercial ships will be able to move through the Arctic, opening shorter shipping routes.
- The ‘northeast passage’ of the region will open up towards Europe.
- The ‘northwest passage’ will head towards the U.S. and Canada.
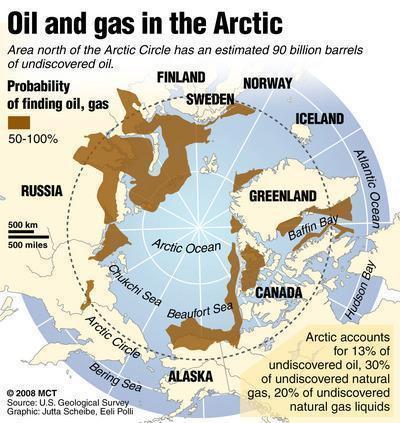
- Resources - It is estimated that beneath the layers of ice, highly prized reservoirs of minerals exist.
- The Arctic is said to possess 30% of the world’s undiscovered natural gas and 13% of its undiscovered oil reserves.
What is China looking for?
- Exploration - China’s 360-degree hunt for resources and new trade routes is taking new turns.
- The new development in the Arctic is reinforcing China's interests in the region.
- China’s obsession with becoming a leading, and advanced, industrial heavyweight is increasingly driving Beijing towards the Arctic.
- It has become unrelenting and undeterred by obstacles posed by geography, politics or technology.
- Projects - The Polar Silk Road (PSR) and Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) initiatives aim at industrialising Eurasia.
- This is aimed through massive infrastructural development and network of trans-continental connectivity.
- China is also focusing on cyber-connectivity.
- This is displayed by its embrace of the digital economy, demonstrated by the rise of the global e-commerce giant Alibaba, or Wechat.
- Talks are on in Chinese government to build a 10,500 km fibre-optic undersea link across the Arctic Circle.
- The enterprise, called the Northeast Passage Cable Project, will provide China a new high-speed digital traffic link.
- The proposal also involves Finland, Japan, Russia and Norway as partners in this undertaking.
- China will get increasingly connected with European financial and data hubs.
- Long term Planning - Beijing’s forays in the Arctic are a result of its long-term planning for deeper engagement with the Arctic.
- China has invested in Iceland following the 2008 financial crisis.
- Eight years later, Chinese company Shenghe Resources purchased 12.5% of Greenland Minerals and Energy.
- China has also signalled its interest in two Iceland ports, as well as Norway’s Arctic Kirkenes port.
What is Russia’s role in this regard?
- Among its littoral countries, Russia claims the largest slice of the Arctic Ocean.
- Coupled with its massive mineral reserves in Siberia, Russia is fast becoming China’s chief natural-resource ally.
- Russia is thus seen as a key to China’s success in the Arctic.
- The state-owned China Development Bank is set to invest in the Russian energy company Novatek.
- Novatek is heading the Arctic LNG II project.
- The deal would provide China access to the Arctic’s liquefied natural gas.
- Significantly, the agreement would open up areas within Russia’s Exclusive Economic Zone in the Arctic where the Chinese can carry out explorations.
Source: The Hindu

